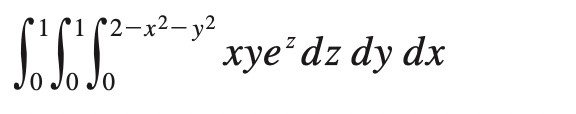Custom Solutions to Stewart Calculus, Integral
Answer
Sure, you came to the right place to get custom solutions given by experts.
For this integral we start by integrating with respect to $z$ : $$ \int _0 ^1 \int _0 ^1 \int_0 ^{2-x^2-y^2} xy e^{z}\,dz\,dy\,dx = \int _0 ^1 \int _0 ^1 xy e^{z}\,\Big]_0 ^{2-x^2-y^2}\,dy\,dx \\ = \int _0 ^1 \int _0 ^1 xy( e^{2-x^2-y^2}-1)\,dy\,dx. $$
Then we do the $y$ integral. For this let $u=2-x^2-y^2$ to get $du=-2ydy$ (remember that in the $y$ integral we treat $x$ as a constant!)
$$ \int _0 ^1 \int _0 ^1 xy( e^{2-x^2-y^2}-1)\,dy\,dx \\ \; \\ =\int _0 ^1 \int _0 ^1 \frac{-1}{2}x (e^{u}-1)\,du\,dx = \int _0 ^1 \frac{-1}{2}x (e^{u}-u)\,\Big]_0 ^1\,du\,dx \\ \; \\ =\int _0 ^1 \frac{-1}{2}x (e-2)\,dx = \frac{-(e-2)}{2}\,\frac{x^2}{2}\,\Big]_0 ^1 = \frac{-(e-2)}{4}$$
- accepted
- 1691 views
- $15.00
Related Questions
- CART Gini cost function
- Banach fixed-point theorem and the map $Tf(x)=\int_0^x f(s)ds $ on $C[0,1]$
- Mechanical principle help (maths)
- Evaluate$\int \sqrt{\tan x}dx$
- Solve only for the multiple choice part, the answer for the first box is 0
- What is f(x). I've been trying to understand it for so long, but I always get different answers, I feel like I'm going crazy. Please someone explain it and read my whole question carefully.
- Prove that $tan x +cot x=sec x csc x$
- Calculus: INFINITE SERIES