Finding values of k for different points of intersection
My question is if you have a question like:
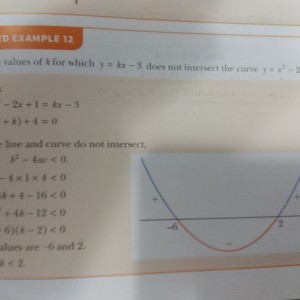
Find the values of K for which $y=kx-3$ does not intersect $y=x^2-2x+1$
To solve it my textbook says to do this.
$x^2-2x+1=kx-3$
$x^2-(2+k)x+4=0$
Then we use the discriminant.
$(2+k)^2-4\times 1\times 4<0$
$k^2+4k-12<0$
$(k+6)(k-2)<0$
So -6 < k < 2
My question is why does this work? What is actually happening for this to work? I've used Desmos and I can't figure out why the -6 < k < 2 part is equal to the resulting equation $k^2+4k-12<0$ between the two points of intersection on the x-axis.
 Math Gnome
Math Gnome
87
Answer
Answers can only be viewed under the following conditions:
- The questioner was satisfied with and accepted the answer, or
- The answer was evaluated as being 100% correct by the judge.
4.8K
The answer is accepted.
Join Matchmaticians Affiliate Marketing
Program to earn up to a 50% commission on every question that your affiliated users ask or answer.
- answered
- 1666 views
- $5.00
Related Questions
- Evaluate $\int_0^{\frac{\pi}{2}}\frac{\sqrt{\sin x}}{\sqrt{\sin x}+\sqrt{\cos x}} dx$
- If both $n$ and $\sqrt{n^2+204n}$ are positive integers, find the maximum value of $𝑛$.
- Algebra Word Problem 1
- Artin-Wedderburn isomorphism of $\mathbb{C}[S_3]$
- A word problem about a rectangular carpet
- Prove that ${n\choose 2}2^{n-2}=\sum\limits_{k=2}^{n}{n\choose k}{k\choose 2}$ for all $n\geq 2$
- Points of intersection between a vertical and horizontal parabola
- Certain isometry overfinite ring is product of isometries over each local factor

Bounty too low!