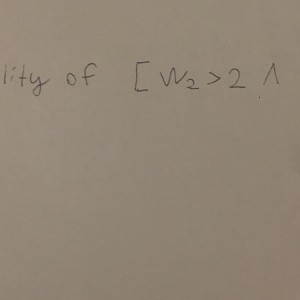Wiener process probability
Calculate with what probability it will happen that the random trajectory of the Wiener process will acquire a value greater than 2 at time 2 and a value less than 2 at time 3.
Answer
- The questioner was satisfied with and accepted the answer, or
- The answer was evaluated as being 100% correct by the judge.
-
Hello, thank you for your answer! Could you please tell me how did you calculate the double integral? Thank you for your response.
-
@Green: Please respond to Kingroma99 question above.
-
@Kingroma99, the double integral was evaluated numerically. Otherwise one can compute it by first treating t as a constant, and integrating from negative infinity to 2-s. This involves the error function, which is the antiderivative of the Gaussian. Then, the result can be integrated with respect to t from 2 to infinity. To get a closed form in terms of error functions, one follows the above procedure while doing a few integral substitutions.
- answered
- 1701 views
- $9.50
Related Questions
- Probability and Statistics question please help
- Borell-Cantelli Lemma application
- Probability
-
Poker Outcomes and Variance: Calculating Likelihood of an Observed Outcome
- What statistical test should I use to compare 2 multiple linear regression models
- Probability of any random n points on a line being within a given distance
- Exercise on Ito's rule for two correlated stocks.
- Mathematical modeling