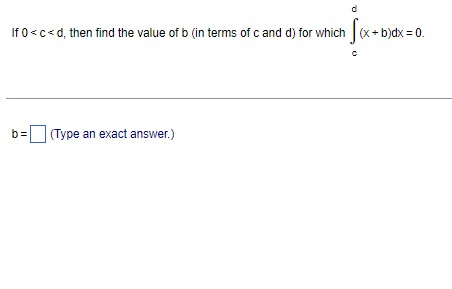Calculus problem
Answer
Answers can only be viewed under the following conditions:
- The questioner was satisfied with and accepted the answer, or
- The answer was evaluated as being 100% correct by the judge.
4.8K
The answer is accepted.
Join Matchmaticians Affiliate Marketing
Program to earn up to a 50% commission on every question that your affiliated users ask or answer.
- answered
- 1396 views
- $15.00
Related Questions
- Help with Business Calculus problem.
- Determine where the following function is discontinuous
- Prove that ${n\choose 2}2^{n-2}=\sum\limits_{k=2}^{n}{n\choose k}{k\choose 2}$ for all $n\geq 2$
- Why does $ \sum\limits_{n=1}^{\infty } 2^{2n} \times \frac{(n!)^2}{n(2n+1)(2n)!} =2 $ ?
- Quick question regarding Analytical Applications of Differentiation
- How to recalculate 2D polygon side lengths when tilt is applied in 3D space?
- Find the derivative of the function $f(x)=\sqrt{\sin^2x+e^x+1}$
- Derivative of $\int_{\sin x}^{x^2} \cos (t)dt$