Confusing Bonus Question
2 Answers
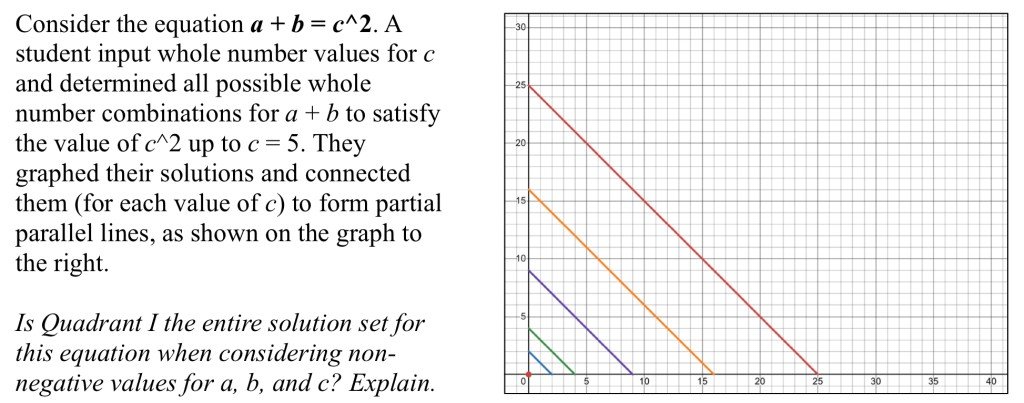
Yes, Quadrant I provides the entire solution set for this question. Indeed for any given $c$, if we let $x=a$ and $y=b$, then $a+b=c^2$, translates to
\[x+y=c^2 \Rightarrow y=-x+c^2\]
which is a line with slope $m=-1$, and $x$-intercept and $y$-intercept are both $c^2$.
For example for $c=5$ you get
\[y=-x+25\]
which is the question of the red line in the image.
-
I think the solutions of the given equation are triples (a,b,c), not pairs (a,b). So the solution set is not Quadrant I, but a 2-dimensional submanifold of $\R^3$, the segment from (c², 0, c) to (0, c², c), for each allowed value of c.
According to the problem statement, I would say that the solutions to the equation are triples $(a,b,c)$, rather than pairs $(a,b)$. So the solution set is $\{ (a, c²-a, c) ~;~ 0 \le a \le c², c \in \R_+ \} = \{ (x, y, \sqrt{x+y}) ~;~ x,y\in \R_+ \} $.
This is a subset of $\R_+^3\subset \R^3$, not of $\R²$, although it is two-dimensional: For each allowed value of $c\in\R_+$, for example $a$ can be chosen in the interval $[0, c²]$ and b is determined as $c²-a$ (or reciprocally). That is, the solutions form the segment (straight line) from $(0, c², c)$ to $(c²,0,c)$. Glueing all these subsets together yields "the first quadrant raised to the height" $z = \sqrt{x+y}$ above a point $(x,y,0)$ on the $\{ z = 0 \}$ plane.
According to the problem statement, it was a choice of the student to consider $c$ as a given parameter for drawing some solutions - that is, the orthogonal projection of these particular solutions $(a,b,c)$ on $\R^2\times\{0\}$, "the first two coordinates" $(a,b)$. But otherwise there is no reason for considering $c$ as a parameter rather than a component of the solution $(a,b,c)$ of the given equation.
 M F H
M F H
- 2 Answers
- 344 views
- Pro Bono
Related Questions
- Differentiate $f(x)=\int_{\sqrt{x}}^{\arcsin x} \ln\theta d \theta$
- What am I doing wrong?
- Vector field
- Equation of the line tangent to a circle
- Algebra Word Problem #1
- Graph the pair of equations in the same rectangular coordinate system: Y=-2x ; y=-2
- Motorcycle Valve Clearance Calculation and Spacer Size Word Problem
- Trash Algebraic Formula
 Do you have any idea what this means and how to solve it? Thanks!
Do you have any idea what this means and how to solve it? Thanks!